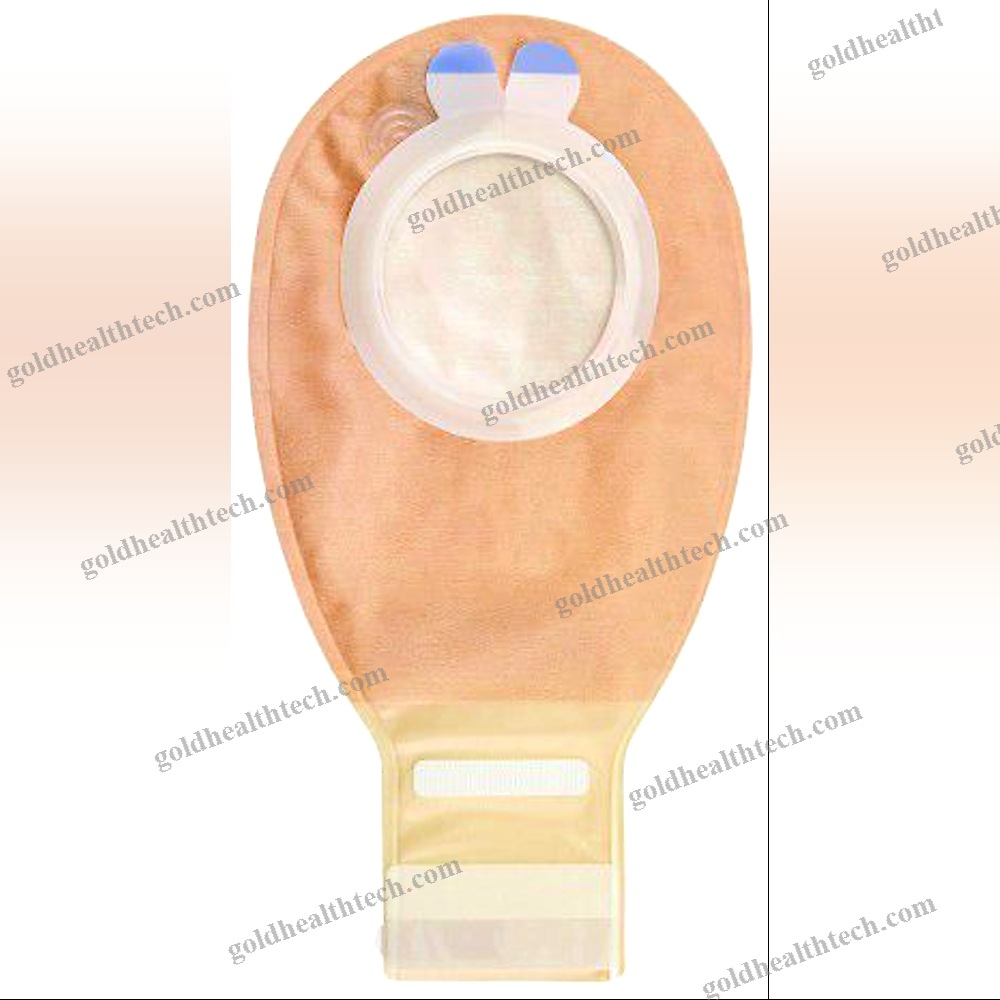
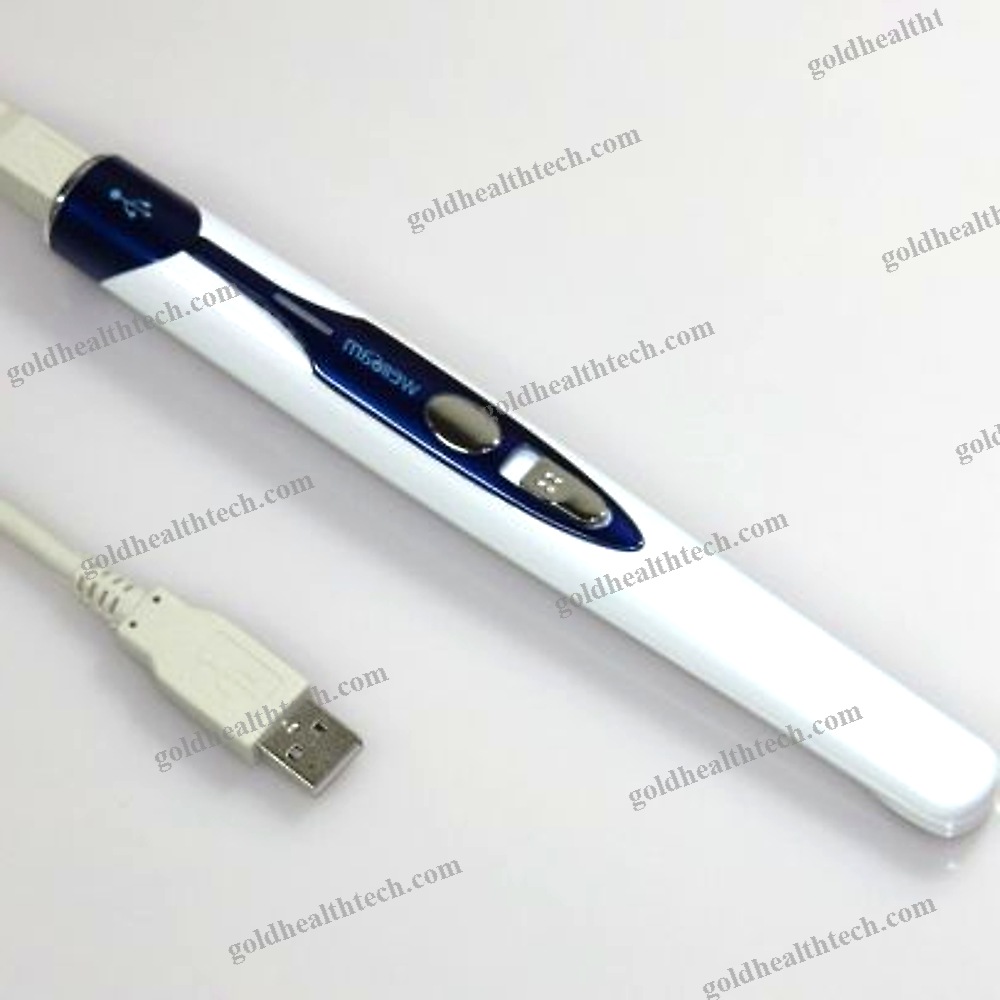
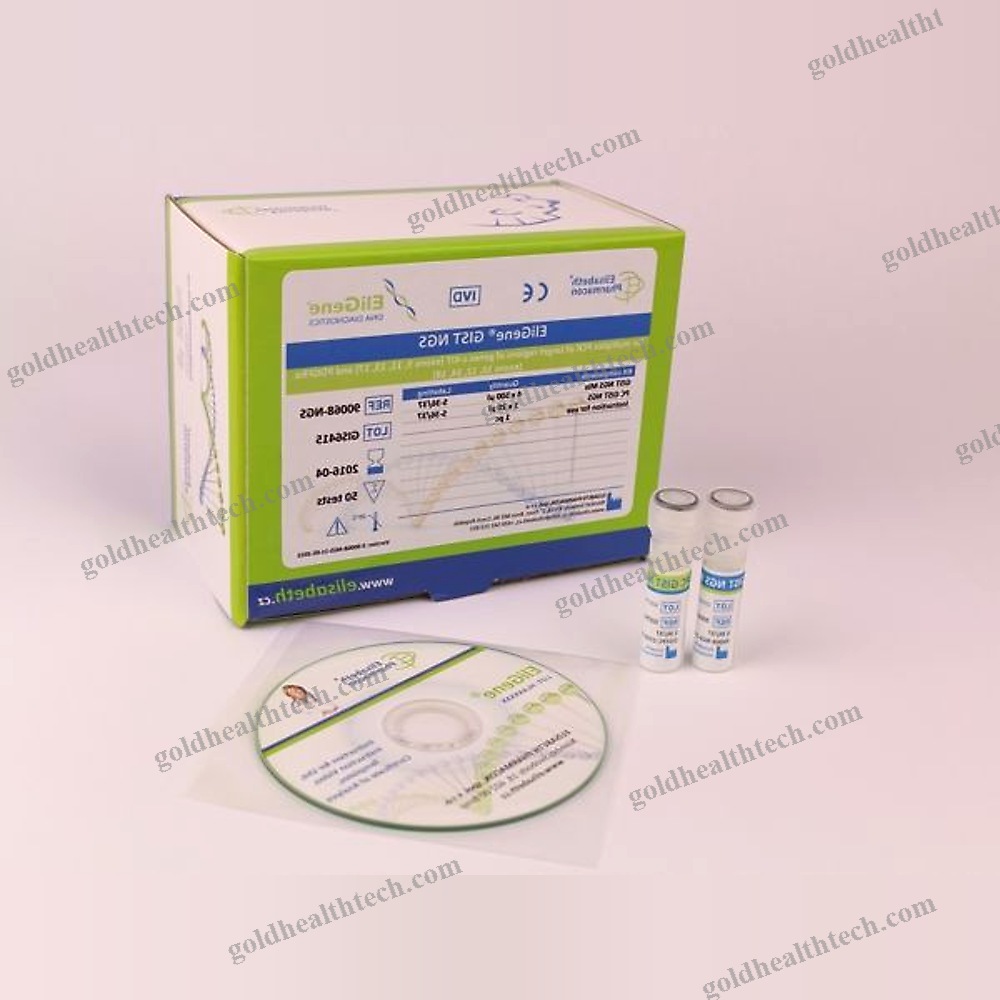
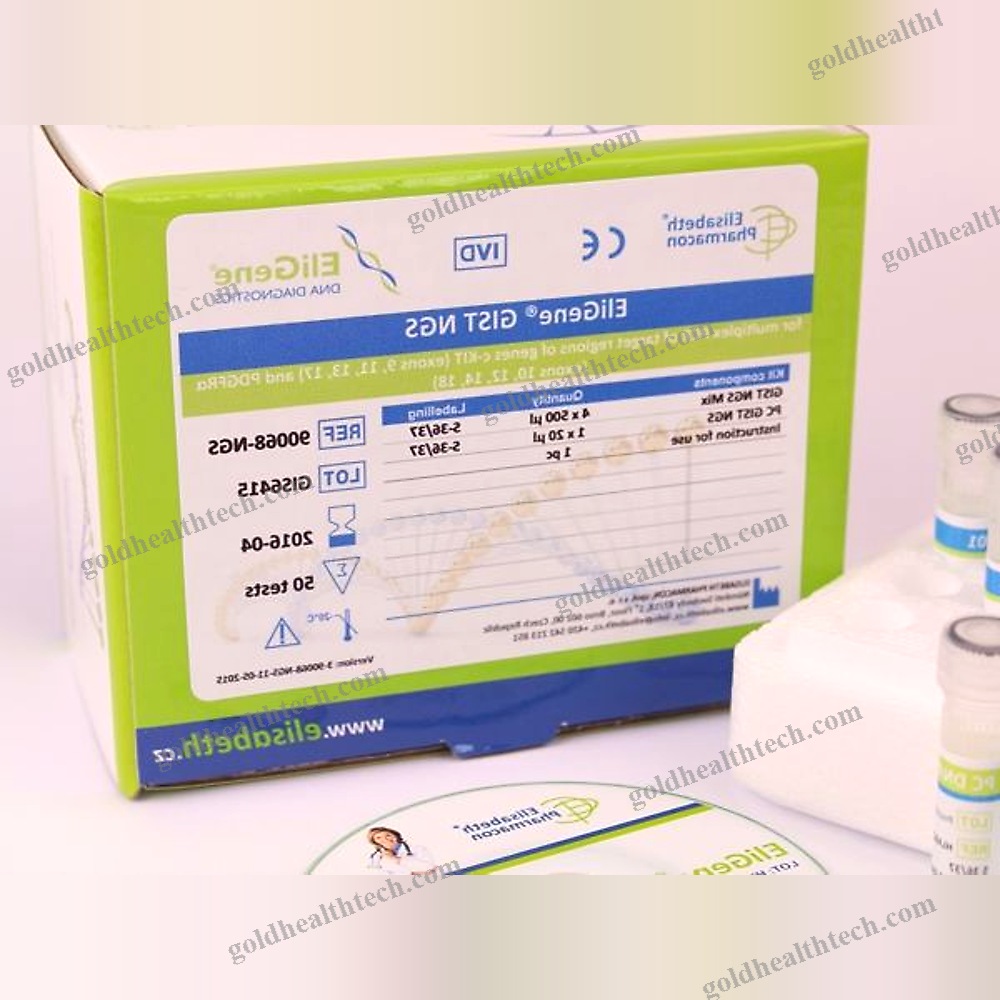
Coagulation Rapid Test
| Sample Type | Plasma, Whole Blood |
| Analysis Mode | Immunochromatographic, Molecular |
| Tested Parameter | Protein, D-Dimer, Thrombin |
| Application Domain | Coagulation |
The HUBI D-Dimer is a rapid, point-of-care test that is based on the immunochromatography assay. It is designed to be used in conjunction with the HUBI-QUANpro to quantitatively determine cross-linked fibrin degradation products (D-Dimers) in citrate or EDTA anticoagulated whole blood or plasma specimens. input:
output:Fibrinogen is the primary protein of the blood coagulation system. The proteolytic removal of both fibrinopeptide A and B by thrombin during the coagulation process converts fibrinogen to soluble fibrin. plasmin digests the fibrin clot, releasing fibrin degradation products with varying molecular weights into the bloodstream. The final product of fibrin degradation is D-dimer, which has a molecular weight of 180 kDa. It is composed of the disulfide bonds that cross-link the remnants of all three chains. A cross-linked region is formed by two isopeptide bonds between the C-terminal parts of g-chains, which maintain the dimeric structure. Patients with atherosclerosis, pulmonary thromboembolism, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and other cardiovascular diseases exhibited elevated levels of D-dimer in their blood.


MAECENAS IACULIS
Vestibulum curae torquent diam diam commodo parturient penatibus nunc dui adipiscing convallis bulum parturient suspendisse parturient a.Parturient in parturient scelerisque nibh lectus quam a natoque adipiscing a vestibulum hendrerit et pharetra fames nunc natoque dui.
ADIPISCING CONVALLIS BULUM
- Vestibulum penatibus nunc dui adipiscing convallis bulum parturient suspendisse.
- Abitur parturient praesent lectus quam a natoque adipiscing a vestibulum hendre.
- Diam parturient dictumst parturient scelerisque nibh lectus.
Scelerisque adipiscing bibendum sem vestibulum et in a a a purus lectus faucibus lobortis tincidunt purus lectus nisl class eros.Condimentum a et ullamcorper dictumst mus et tristique elementum nam inceptos hac parturient scelerisque vestibulum amet elit ut volutpat.